MD Page Theory prefinal: Difference between revisions
SnakeTuning (talk | contribs) No edit summary Tag: wikieditor |
SnakeTuning (talk | contribs) Tag: wikieditor |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==VR Conditioner== | ==VR Conditioner== | ||
[[File:Conditioneer_temp.png|ECU | [[File:Conditioneer_temp.png|ECU Daughter-board|left|thumb]] | ||
A daughter-board, known as the VR Conditioner, is installed in the Honda ECU to process these high-voltage signals, converting them into a more manageable 0-5V range. The distinctive feature of this VR Conditioner is its adaptive sensitivity reduction to the input voltage from the inductive sensors as the engine RPM increases. | |||
This is a logical approach for handling inductive sensors as the input voltage can change significantly—over an order of magnitude. However, this poses a significant problem when emulating distributor functions. The accuracy and correctness of ignition calculations are highly sensitive to the input voltage at the ECU. If the voltage is too low, the ECU begins to "float," and if it drops significantly, the ECU starts to "miss" gear teeth. | |||
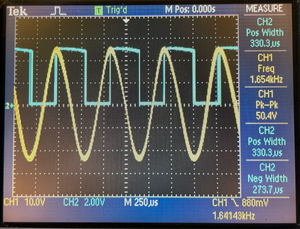
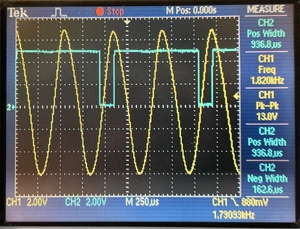
Oscilloscope traces illustrate two scenarios: normal voltage at 8000 RPM and reduced voltage where signals are missed every other tooth. The blue trace shows the output from the conditioner, and the yellow trace is the input from the sensor. This visualization helps in understanding the need for stable input voltage for accurate ignition timing. | |||
[[File:Ign_OK.png|Correct Ignition|right|thumb]] | [[File:Ign_OK.png|Correct Ignition|right|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Ign_Fault.png|Fault Ignition|right|thumb]] | [[File:Ign_Fault.png|Fault Ignition|right|thumb]] | ||
Revision as of 08:42, 31 May 2024
Distributor
In the distributors of Honda B, D, F, and H Series engines, there are three Variable Reluctance Sensors: CKP, TDC, and CYP. The voltage across these sensors varies with the engine's RPM, ranging from approximately ±5V to ±60V.
VR Sensors are crucial in these systems for detecting engine parameters. Unlike modern Hall sensors, which provide a digital output, VR Sensors produce an analog signal whose amplitude varies with the speed of the engine. This variability can lead to signal integrity issues at high RPMs, where precision is critical for efficient engine performance.
VR Conditioner
A daughter-board, known as the VR Conditioner, is installed in the Honda ECU to process these high-voltage signals, converting them into a more manageable 0-5V range. The distinctive feature of this VR Conditioner is its adaptive sensitivity reduction to the input voltage from the inductive sensors as the engine RPM increases. This is a logical approach for handling inductive sensors as the input voltage can change significantly—over an order of magnitude. However, this poses a significant problem when emulating distributor functions. The accuracy and correctness of ignition calculations are highly sensitive to the input voltage at the ECU. If the voltage is too low, the ECU begins to "float," and if it drops significantly, the ECU starts to "miss" gear teeth. Oscilloscope traces illustrate two scenarios: normal voltage at 8000 RPM and reduced voltage where signals are missed every other tooth. The blue trace shows the output from the conditioner, and the yellow trace is the input from the sensor. This visualization helps in understanding the need for stable input voltage for accurate ignition timing.
Distributor Removal
Для эмуляции сигналов трамблера конечно же можно сделать электрическое устройство, которое будет имитировать работу VR датчиков, но особенности работы VR датчиков и двойное преобразование сигнала из низковольтного в высоковольтный и обратно крайне негативно скажется на точности зажигания на высоких оборотах. Кроме того при высоковольтной эмуляции будет невозможно работать с Aftermarket ECUs без дополнительных преобразователей сигналов обратнов низковольтные.
Детально изучив принципы работы VR кондиционера Эбу Хонда инженеры SnakeTuning нашли и запатентовали (Patent pending) более простое и эффективное решение этой задачи - «Заблокировать» адаптивность VR кондиционера, что позволит ЭБУ работать с низковольтными сигналами.
Идея доработки состоит в том, что в цифровых схемах и микропроцессорных устройствах входные данные можно запоминать различными способами, а вот в аналоговых схемах запоминающим элементом может быть только конденсатор. В данном случае, конденсатор "запоминает" уровень напряжения, соответствующий частоте вращения двигателя, а внутренняя схема ЭБУ Honda меняет входную чувствительность, в зависимости от напряжения на "запоминающем" конденсаторе.
Достаточно найти 3 "запоминающих" конденсатора (по одному на каждый датчик) и закоротить их перемычками, чтобы напряжение на них не поднималось при увеличении оборотов двигателя и чувствительность ЭБУ всегда была максимальной.